What is a Cloud Application? Definition, Pros & Cons + Examples
Cloud applications are fascinating.
They're the innovative solutions reshaping how we interact with technology in business and everyday life.
What exactly are cloud applications?
They are software programs that utilize cloud-based resources, offering unparalleled accessibility, efficiency, and scalability.
We'll explore these applications' substantial benefits, such as reduced IT costs, improved collaboration, and enhanced flexibility.
Conversely, we'll also address potential challenges and provide strategies for mitigating them, especially concerning data security and compliance.
Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, understanding and leveraging cloud applications is crucial in today's fast-paced, digitally-driven world.
This article is your guide to making informed decisions in the cloud computing landscape, paving the way for innovation and growth in your organization.
Understanding Cloud Applications
The term 'cloud application' is a fundamental component of modern computing.
A cloud application, or cloud app, is software that operates in the cloud.
Unlike traditional applications that are stored and run on your local device, a cloud app is hosted on remote servers and accessed over the Internet.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Applications
- Accessibility: A standout feature of cloud applications is their accessibility. You can access them from anywhere, anytime, with an internet connection. This flexibility is a game-changer, especially when remote work and digital collaboration are becoming the norm.
- Scalability: Cloud applications are incredibly scalable. This means they can easily accommodate the changing needs of a business. Whether scaling up or down, cloud apps adjust seamlessly, ensuring you have the right resources without overspending.
- Maintenance and Updates: With cloud-based applications, the burden of maintenance and updates shifts from the user to the service provider. This aspect not only eases the workload on your end but also ensures you're always using the latest, most secure version of the software.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By using cloud applications, businesses can save significantly on costs. There's no need for heavy upfront investments in hardware or worries about ongoing maintenance costs. You typically pay for what you use, making it a financially savvy choice, especially for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Integration and Customization: Cloud applications often have the added advantage of easy integration with other services and platforms. Many also offer customization options, allowing them to be tailored to specific business needs.
- Security: While there are concerns around cloud security, reputable cloud service providers invest heavily in securing their infrastructures. Cloud applications often have robust security measures, including regular backups and strong data encryption, providing peace of mind for sensitive business data.
Cloud applications bring convenience, efficiency, and scalability to the table.
They are integral to cloud computing, reshaping how businesses and individuals interact with technology.
As we delve deeper into the digital era, understanding and leveraging the power of cloud applications is not just an option; it's necessary for staying competitive and agile in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
Types of Cloud Applications
When exploring the diverse world of cloud applications, you'll encounter various types, each serving distinct needs and functionalities. Primarily, these are SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Here's a closer look:
Software as a Service (SaaS)
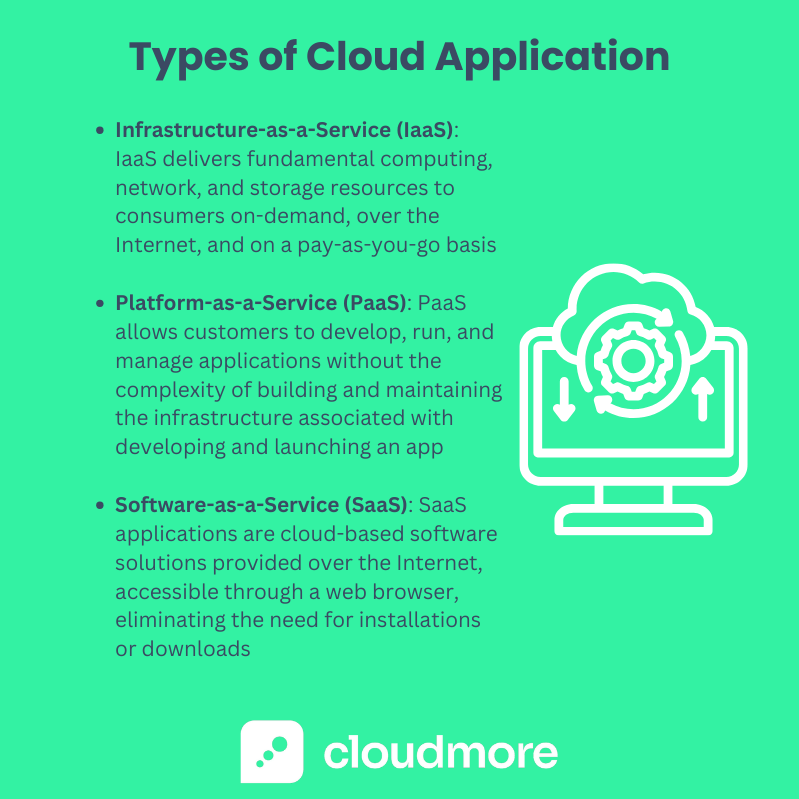
Definition: SaaS applications are cloud-based software solutions provided over the Internet. They're readily accessible through a web browser, eliminating the need for installations or downloads.
Examples:
- Google Workspace for collaborative office tasks
- Salesforce for customer relationship management
- Dropbox for cloud storage and file sharing
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Definition: PaaS provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app.
Examples:
- Heroku offers a platform for app development and deployment
- Microsoft Azure, facilitating a range of app development tools
- Red Hat OpenShift is known for its enterprise-level application hosting.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Definition: IaaS delivers fundamental computing, network, and storage resources to consumers on-demand, over the Internet, and on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Examples:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides scalable cloud computing solutions
- Google Cloud Platform, offering a suite of cloud computing services
- IBM Cloud, known for its high-performance cloud infrastructure services
Understanding these types will help you make more informed decisions about the cloud-based applications and services best suited to your needs.
Whether it's managing data, developing unique applications, or leveraging existing software solutions, there's a cloud application type ready to propel your endeavors into new heights of efficiency and innovation.
How Cloud Applications Work
Grasping the technicalities behind cloud applications can be challenging, but a basic understanding is essential in today's cloud-centric world.
These applications work differently from traditional software, leveraging the power and versatility of cloud computing to offer unique advantages.
Cloud Application Architecture and Its Components
- Front-End Interface: This is what you, as a user, interact with. It can be a web browser or an app installed on your device. The interface is designed for easy use, ensuring seamless access to the application's features.
- Back-End Servers: The back-end includes various servers and computers where the processing occurs. These servers store data and run the application's core functionalities. They are the powerhouse of the cloud application.
- Database Management: Cloud applications often require a robust database to store and manage data. This database is hosted in the cloud, ensuring data is easily accessible and secure.
- Middleware: Middleware allows communication and data management between the front-end and back-end of the cloud application. It includes various tools and services that ensure the smooth operation of the application.
- Network and Internet Connectivity: None of this would be possible without a network and internet connectivity. This component connects your device with the cloud service, enabling data transfer and application functionality.
- Cloud Resources: These are the virtual resources provided by the cloud service provider. They can be scaled up or down based on the application's demand, offering flexibility and scalability.
By understanding the architecture and components of cloud applications, you gain insight into how these powerful tools function. This knowledge can help you choose and use suitable cloud applications more effectively, enhancing your business operations or personal productivity in the cloud.
Benefits of Cloud Applications
Cloud applications offer a myriad of advantages that are transforming how businesses operate. From enhanced efficiency to cost savings, the benefits are substantial.
Here's a glimpse into some key advantages:
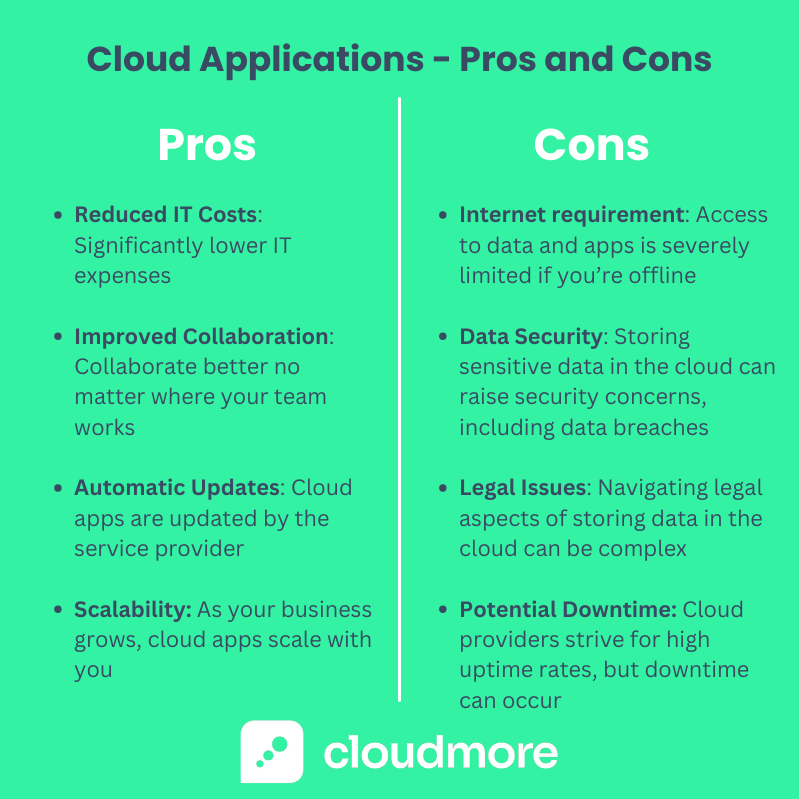
- Reduced IT Costs: Cloud applications can significantly lower your IT expenses. There's no need for substantial upfront investments in hardware or software. Plus, the pay-as-you-go model of many cloud services helps in budget management.
- Improved Collaboration: Cloud applications enhance collaboration whether your team is based in the same office or works globally. Tools like cloud-based document sharing and real-time editing make teamwork effortless and productive.
- Flexibility and Mobility: With cloud apps, your business isn't tied to a single location. Employees can access data and applications from anywhere, using any device with internet connectivity. This mobility is crucial in today's dynamic work environments.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud applications are updated automatically by the service provider. This ensures you're always using the most current version and reduces the burden on your IT staff.
- Scalability: As your business grows, your cloud applications can quickly scale with you. You can increase storage, enhance features, or add users without a hitch.
- Enhanced Security: Reputable cloud applications come with high levels of security. Providers often implement strict security measures, including data encryption and regular security audits.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud applications improve your business's resilience. Data stored in the cloud makes it easier to recover information in case of hardware failure, natural disaster, or other disruptions.
Drawbacks of Cloud Applications
While cloud applications bring numerous benefits, they also come with their own set of challenges. Awareness of these potential issues is essential to ensure a smooth and secure cloud experience.
- Dependency on Internet Connectivity: Cloud applications rely heavily on an Internet connection. Without it, access to your data and applications can be severely limited.
- Data Security Concerns: Storing sensitive data in the cloud can raise security concerns. Data breaches and unauthorized access are a significant worry for many businesses.
- Limited Customization and Control: Depending on the cloud service provider, customization and control over the application and data may be limited.
- Compliance and Legal Issues: Navigating the legal and compliance aspects of storing data in the cloud can be complex, especially in different regions or countries.
- Potential Downtime: While cloud providers strive for high uptime rates, occasional downtime can occur, which might impact your business operations.
- Cost Overruns: Without proper management, cloud services can lead to unexpected expenses, mainly if the pricing structure is complex or there's unchecked resource use.
Popular Cloud Application Examples
Cloud applications have become ubiquitous in our digital world, with many becoming household names. Here's a look at some of the well-known cloud applications that are shaping various industries:
Google Workspace
An integrated suite of secure, cloud-native collaboration and productivity apps powered by Google AI. Includes Gmail, Docs, Drive, Calendar, Meet, and more.
Salesforce
A leading customer relationship management (CRM) cloud application that helps businesses connect with their customers, streamline processes, and improve profitability.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
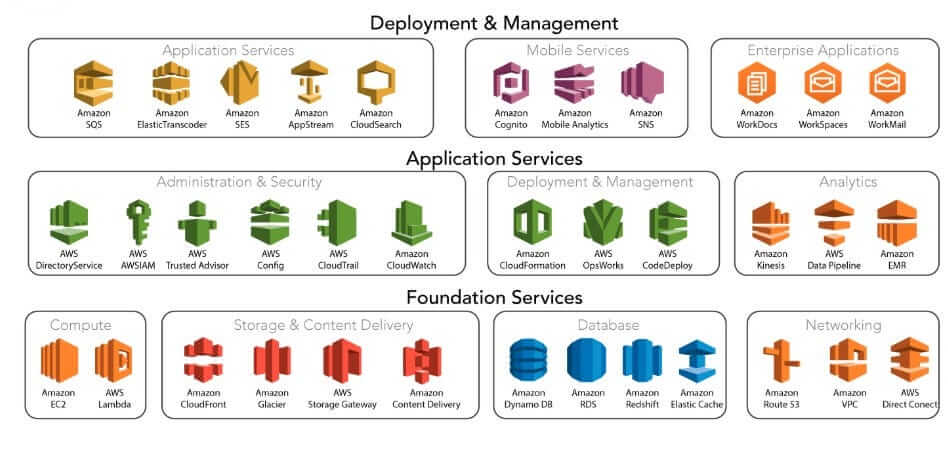
A comprehensive and broadly adopted cloud platform that offers over 175 fully featured services from data centers globally.
Microsoft Azure
A cloud computing service for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications and services through Microsoft-managed data centers.
Dropbox
A file hosting service offering cloud storage, file synchronization, personal cloud, and client software.
Choosing the Right Cloud Application for Your Business
Selecting the correct cloud application can be a game-changer for your business. It's about finding a solution aligning with your needs and goals. Consider the following factors:
- Business Objectives: Identify what you want to achieve with the cloud application. Is it for improving collaboration, increasing efficiency, or data management?
- Scalability: Ensure the application can scale in line with your business growth. Look for flexible solutions regarding user numbers, storage, and functionalities.
- Integration Capabilities: The cloud application should seamlessly integrate with your existing systems and software to ensure a smooth workflow.
- Security and Compliance: Assess the cloud application's security measures and compliance standards, especially if you handle sensitive data. When assessing cloud application solutions, it's essential to evaluate each provider’s approach to securing sensitive data, considering new threats like advanced persistent attacks, ransomware, and compliance risks
- Cost: Evaluate the pricing structure. Consider not just the initial costs but also long-term expenses and potential savings.
- User Experience: The application should be user-friendly and require minimal training for your team.
- Vendor Reputation and Support: Choose a provider with a strong reputation and reliable customer support.
- Custom Cloud Application Development: Sometimes, off-the-shelf solutions might not fit your unique requirements. In such cases, consider custom cloud application development. It offers tailored solutions designed specifically for your business processes and needs.

Making an informed decision in choosing the right cloud application will position your business for efficiency and growth. It's not just about adopting technology; it's about enhancing your business strategy.
Key Takeaways about Cloud Applications
As we reach the end of our exploration into the world of cloud applications, let's recap the key insights:
- Cloud Applications are Transformative: They offer unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, revolutionizing how businesses operate.
- Variety and Versatility: From SaaS to PaaS and IaaS, cloud applications cater to diverse needs, empowering industries from healthcare to retail with tailored solutions.
- Accessibility and Efficiency: Cloud applications provide easy access from anywhere, streamlining collaboration and workflow.
- Security and Maintenance: While security is a concern, reputable providers ensure robust protection. Plus, maintenance is more straightforward and less time-consuming.
- Making the Right Choice: Selecting the right cloud application is crucial. It involves understanding your business needs, scalability, integration capabilities, and cost considerations.
- Custom Solutions: Custom cloud application development can be a game-changer for specific needs, offering solutions tailored to your unique business processes.
Embracing cloud applications can propel your business into a future of enhanced efficiency, innovation, and growth. As you move forward, consider how cloud technology can be integrated into your business strategy. The potential is immense, and with the right tools and understanding, the sky's the limit.
Share this
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Public vs Private Cloud - Key Differences & Examples

AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud - Key Cloud Services Comparison


