Microsoft Direct vs Indirect CSP: Key Differences, Pros, Cons
Navigating the cloud ecosystem, Microsoft's Cloud Solution Provider (CSP) Program stands out as pivotal for businesses looking to harness the power of cloud services.
This program is not just an avenue for offering Microsoft's extensive suite of cloud solutions; it's a strategic decision point that shapes how you connect with customers, manage your offerings, and scale your operations.
Within this landscape, choosing between a direct and indirect CSP model becomes a critical business decision, with each path offering distinct advantages, challenges, and opportunities.
Understanding the nuances of these models can significantly impact your market approach, profit margins, and customer relationships.
We'll explain the key differences between Direct and Indirect CSPs, discuss factors to consider in making your choice, and make recommendations tailored to your business size and objectives.
Direct CSP - An Overview
Understanding the Direct CSP model is crucial when venturing into the Microsoft CSP landscape.
Direct CSPs are partners authorized directly by Microsoft to sell cloud services.
This model offers a more hands-on approach, allowing businesses to purchase directly from a provider that manages the entire customer lifecycle.
Key Characteristics and Requirements of Direct CSPs
- Direct Relationship with Microsoft: One of the defining characteristics of Direct CSPs is their direct billing and support relationship with Microsoft. This direct line simplifies processes and enhances the quality of service you receive.
- Infrastructure Requirements: As a Direct CSP, the provider must be able to manage end-to-end customer support and billing. This means having a robust infrastructure to handle customer queries, technical support, and seamless billing processes.
- Expertise and Resources: Direct CSPs must offer added value through their expertise in Microsoft products and services. This includes having a knowledgeable team to deliver tailored solutions and proactive customer support.
- Commitment to Microsoft: Direct CSP partners must meet specific performance thresholds, including sales targets and customer acquisition goals. This commitment ensures that Direct CSPs will promote and support Microsoft products effectively.
By choosing a Direct CSP, you're opting for a model that offers direct access to Microsoft's products and services alongside specialized support tailored to your business needs.
It's a partnership that facilitates your access to cloud solutions and supports your journey with expert guidance and a comprehensive service model.
Indirect CSP - An Overview
The Indirect CSP model offers a unique pathway for businesses to sell Microsoft's cloud services in the landscape of Microsoft CSPs.
Unlike Direct CSPs that work directly with Microsoft, Indirect CSPs operate through a symbiotic relationship with Microsoft-authorized distributors.
This model is for those who prefer to offer Microsoft's suite of cloud services to their customers without the complexities of direct billing and support.
Key Characteristics and Requirements of Indirect CSPs
- Flexibility and Support: Indirect CSPs benefit from a flexible business model. They rely on CSP distributors or Microsoft indirect resellers to manage the intricate details of billing, provisioning, and support. This allows businesses to focus on sales and customer service while leveraging the expertise of their partners.
- Lower Barriers to Entry: Joining the Indirect CSP program requires less upfront investment than the Direct model. Businesses don't need to prove extensive technical capabilities or invest in support infrastructure, making it attractive for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or those just beginning their journey in cloud services.
- Partnership and Ecosystem: Being an Indirect CSP means becoming part of a larger ecosystem. Indirect CSPs must choose their distributor partner wisely, as this relationship is crucial. This partnership is pivotal in scaling your business and expanding your cloud solutions portfolio.
- Commitment to Growth: While the entry requirements might be lower, success as an Indirect CSP demands a commitment to growth and sales. Distributors often provide sales targets and incentives to encourage expansion.
Indirect CSPs bridge Microsoft's comprehensive cloud services and customers, offering a pathway to cloud business with reduced complexity and increased support.
For many, it represents the perfect balance between autonomy in customer relations and reliance on the robust infrastructure of partners.
If your business is keen on providing Microsoft cloud solutions without the overhead of direct management, becoming an Indirect CSP could be your next strategic move.
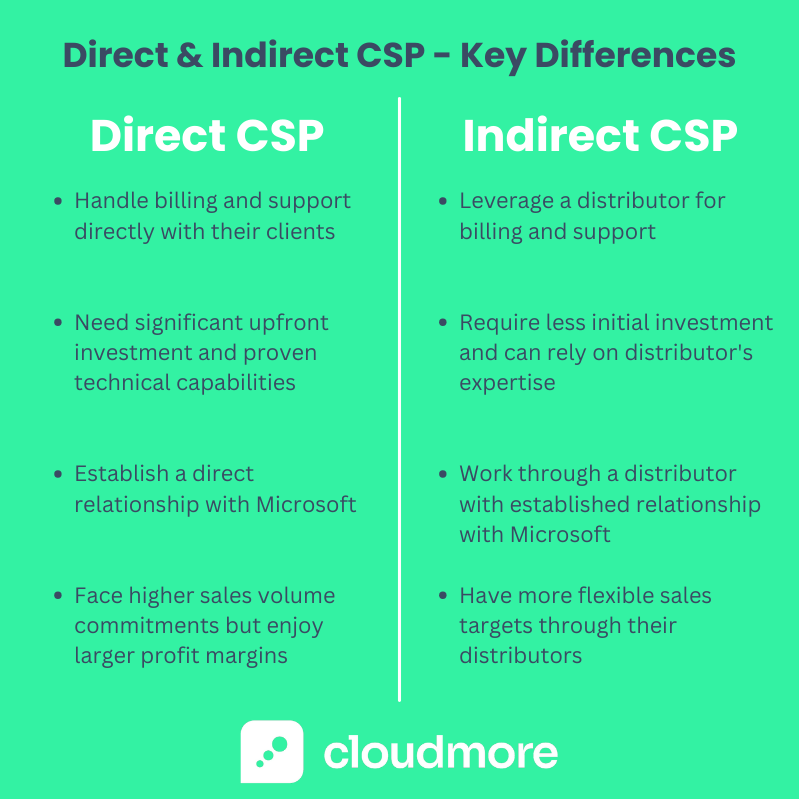
Key Differences Between Direct and Indirect CSP
Understanding the distinctions between Direct and Indirect models is crucial when navigating the Microsoft CSP landscape. Here's a concise comparison to guide you:
- Billing and Customer Support:
- Direct CSPs handle billing and customer support directly with their clients, requiring robust infrastructure and resources.
- Indirect CSPs leverage their distributor for billing and support, easing operational demands. 
- Initial Investment and Capabilities:
- Direct CSPs need significant upfront investment and proven technical capabilities to manage and support Microsoft Cloud solutions.
- Indirect CSPs require less initial investment and can rely on their distributor's expertise and infrastructure.
- Partnership Model:
- Direct CSPs establish a direct relationship with Microsoft, gaining access to comprehensive resources, support, and training.
- Indirect CSPs work through a distributor, benefiting from the distributor's established relationship with Microsoft and additional support services.
- Sales Volume and Scale:
- Direct CSPs often face higher sales volume commitments but enjoy larger profit margins due to direct dealings.
- Indirect CSPs may have more flexible sales targets through their distributors, which suits businesses of varying sizes.
- Market Focus and Strategy:
- Direct CSPs typically cater to a more extensive market segment, leveraging their capacity to offer customized solutions.
- Indirect CSPs are well-suited for SMBs or those focusing on specific market niches, benefiting from the distributor's reach and support.
Pros and Cons of Direct and Indirect CSP
Choosing between Direct and Indirect CSP models is a significant decision for businesses aiming to offer Microsoft cloud solutions.
Each path presents unique advantages and challenges that can impact your operational efficiency and growth potential.
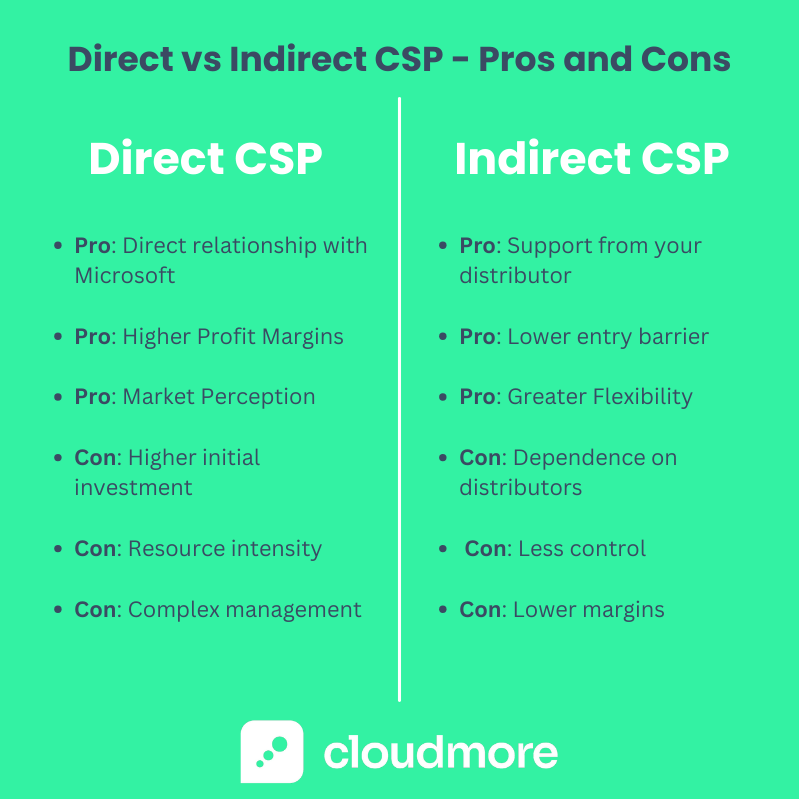
Advantages of Direct CSP
- Direct Relationship with Microsoft: Gain firsthand access to Microsoft's resources, support, and training programs, ensuring you're always at the forefront of cloud services.
- Higher Profit Margins: Managing sales and billing directly allows for greater control over pricing and potentially higher margins.
- Customization and Control: Direct CSPs can offer more tailored solutions and direct customer support, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Market Perception: Being a Direct CSP can elevate your brand, as it reflects a strong partnership with Microsoft and a high level of expertise.
Disadvantages of Direct CSP
- Higher Initial Investment: Requires a substantial upfront investment in infrastructure, support systems, and technical capabilities.
- Resource Intensity: Direct CSPs must manage all customer support and billing in-house, demanding more time and resources.
- Sales Volume Commitments: Often involves higher sales volume commitments to Microsoft, which can be challenging for smaller businesses.
- Complex Management: Managing the direct relationship with Microsoft and all customer interactions can become complex and resource-intensive.
Advantages of Indirect CSP
- Lower Entry Barriers: Starting with less upfront investment and no need for an extensive technical infrastructure is easier.
- Support from Distributors: Benefit from the distributor's expertise in billing, support, and technical issues, allowing you to focus on sales and customer relationships.
- Flexibility: Ideal for businesses with varying customer demands, as it allows for scaling up or down without significant infrastructure changes.
- Broader Ecosystem: Access to a wider ecosystem of services and support through the distributor, enhancing your offerings.
Disadvantages of Indirect CSP
- Dependence on Distributors: Your business model and offerings may be influenced by the capabilities and limitations of your chosen distributor.
- Lower Margins: The involvement of a distributor means your margins may be lower compared to the Direct CSP model.
- Less Control: Less direct control over the customer experience and billing process can impact customer satisfaction.
- Market Perception: Some customers may prefer to work directly with CSPs that have a direct relationship with Microsoft.
Whether you opt for the Direct or Indirect CSP model, understanding these pros and cons is crucial to making an informed decision that aligns with your business strategy and capabilities.
Choosing the Right CSP Model for Your Business
Deciding between a Direct and Indirect CSP model is pivotal for businesses planning to venture into or expand within the Microsoft cloud ecosystem.
This choice will significantly influence your operational structure, customer engagement, and growth trajectory.
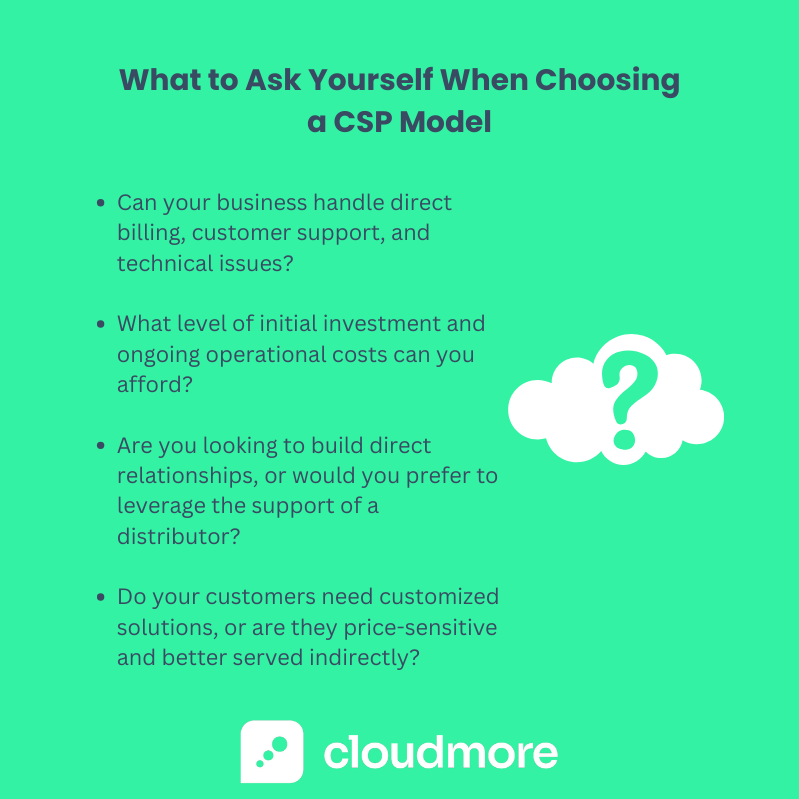
Factors to Consider
When evaluating the best CSP model for your business, several key factors come into play:
- Technical and Operational Capabilities: Assess your current infrastructure and technical expertise. Can your business handle direct billing, customer support, and technical issues?
- Financial Resources: Consider each model's initial investment and ongoing operational costs.
- Business Model and Objectives: Are you looking to build direct relationships, or would you prefer to leverage the support and infrastructure of a distributor?
- Growth Strategy: Consider how fast you want to grow – Direct CSPs often provide higher margins and greater control, which is preferable for rapid scaling.
- Market and Customer Base: Identify your target market and customer base. Do your customers require customized solutions and direct interactions, or are they price-sensitive and potentially better served through an Indirect model?
Recommendations Based on Business Size and Needs
- Small to Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs): If you're an SMB with limited resources or new to cloud services, starting as an Indirect CSP can help you leverage a distributor's existing infrastructure and support. This allows you to build relationships without the heavy lifting of direct support and billing.
- Businesses with Established Cloud Expertise: If your business has a strong foundation in cloud services and technical support and wants to expand its offerings directly to customers, the Direct CSP model may be a better fit.
- Rapidly Scaling Enterprises: For businesses in rapid growth phases with the financial resources to support expansion, the Direct CSP model provides the infrastructure and control necessary to scale efficiently. Direct relationships with Microsoft and customers can foster more robust business development.
- Niche Market Focus: If your business focuses on a specific niche or industry, consider the Indirect CSP model to benefit from the distributor's specialized support and services.
Choosing the suitable CSP model is a strategic decision that requires careful consideration of your business's current capabilities, resources, and growth aspirations.
Whether you opt for the Direct or Indirect path, ensure your choice aligns with your long-term objectives and allows you to effectively deliver value to your customers.
Key Takeaways about Direct vs Indirect CSP
Choosing the right Microsoft CSP model—Direct or Indirect—can significantly impact how your business offers and manages Microsoft's cloud solutions.
Here's a brief recap of the main points to consider:
- Direct CSPs establish a direct relationship with Microsoft, necessitating a substantial initial investment but offering higher margins, more control, and the ability to provide customized solutions directly to customers.
- Indirect CSPs partner with distributors to leverage their infrastructure for billing and support, requiring less upfront investment and allowing businesses to focus on sales and customer service without the overhead of direct management.
- Consider your business's technical and operational capabilities, financial resources, growth strategy, and the needs of your target market.
- Recommendations vary based on business size and needs, with indirect CSPs often being more suitable for SMBs or those new to cloud services, and direct CSPs are better for businesses with established cloud expertise or those aiming for rapid scaling.
Embarking on the CSP journey presents an opportunity to expand your business and deepen your relationship with Microsoft and your customers.
Whether you choose the Direct or Indirect path, the CSP program opens doors to a wide array of cloud services and solutions that can transform businesses' operations and innovation.
Share this
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Changes to the Microsoft CSP Direct Program

Before You Step Back from Direct CSP: What You Really Give Away



